Course Content
Project management and its operating environment
- Define of project and project management
- Vital purpose and definition of programme management, project management, and portfolio management
- Difference between programme management and portfolio management in the field of project management
- Differentiate between project and business
- Pros of effective project management
- Know about Project environment
- Learn about PESTLE as a tool
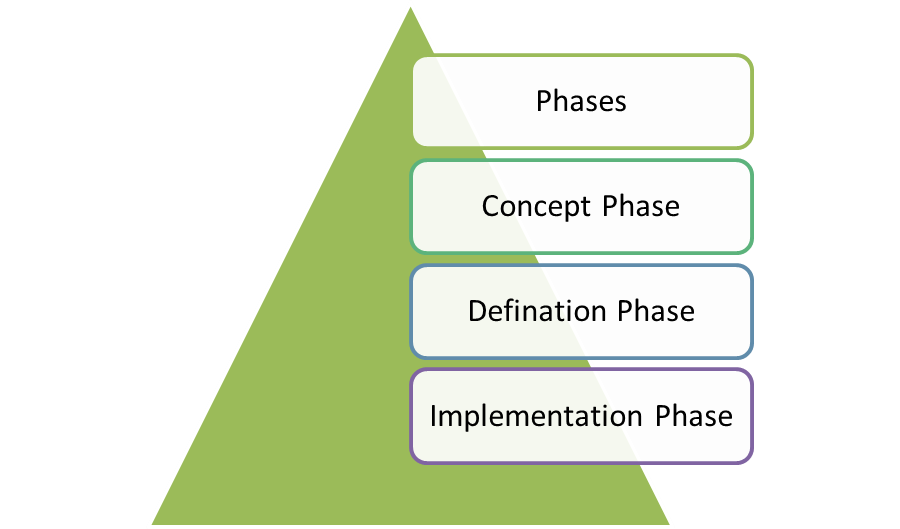
Project Concept Phase
- Stakeholder management
- Project success management
- Business case
- Its benefits
Project Definition Phase
- Project management plan
- Learn Quality Management
- Risk management
- Scope management
- To Scheduling
- Resource management
- To Estimating
- Define Procurement
Project Management in Context
- Project management
- Programme management
- Portfolio management
- Project context
- Project sponsorship
Planning the Strategy
- Project quality
- Project risk management
- Purpose of the project management plan (pmp)
- Handle Stakeholders’ Management
- Project success and benefits management
Executing the Strategy
- Scope management
- Scheduling
- Resource management
- Change control information
- Management and reporting
- Issues management
Techniques
- Configuration management
- Estimating
- Project business case
- Procurement
Organising and Governance
- Project lifecycle
- Handover and closeout
- Project reviews
- Organisational roles
People and the Profession
- Communications in a project
- Teamwork
- Leadership
Scope management
- Define scope management
- Product Breakdown Structure and Work Breakdown Structure
- Configuration
- Change control
- Links between configuration and change control
- Process of Change control
- Configure management process
Scheduling and resource management
- Define Total float and critical path
- Understand Gantt chart, milestone, and baseline
- Know Resource Management
- Understand different Types of resources
- Resource smoothing/resource levelling
- Procurement
Risk management and issue management
- Project risk and risk management
- Project risk management process
- Use of risk register
- Issue and issue management
- Use of issue log
- Escalation process
Project quality management
- Quality and quality management
- Quality planning, quality assurance, quality control, and continual improvement
- Differences b/w quality control and assurance
- Project reviews such as
- Gate post
- Benefit
- Peer reviews
Communication
- Methods of communication
- Barriers to communication
- Effective communication
- Communication plan

 ENQUIRE
ENQUIRE
 REQUEST CALLBACK
REQUEST CALLBACK
 GET A FREE QUOTE
GET A FREE QUOTE


 Introduction
Introduction Course Details
Course Details Course Content
Course Content



 London
London