Course Content
Introduction and Overview
- Define Continual Service Improvement
- Scope and goals of CSI
- Objective and purpose of CSI
- How to embed CSI into organisational processes
- How to create business value
- CSI approach
Principles of Continual Service Improvement
- Establish accountability
- Introduction to unambiguous ownership and its roles
- Support CSI application and register
- Service Level Management and CSI
- Provide adequate governance
- Knowledge management
- Apply or implement CSI with the Demand cycle
- Service Measurement
- Ensure effective governance with CSI
- Support CSI with frameworks, models, standards and quality systems
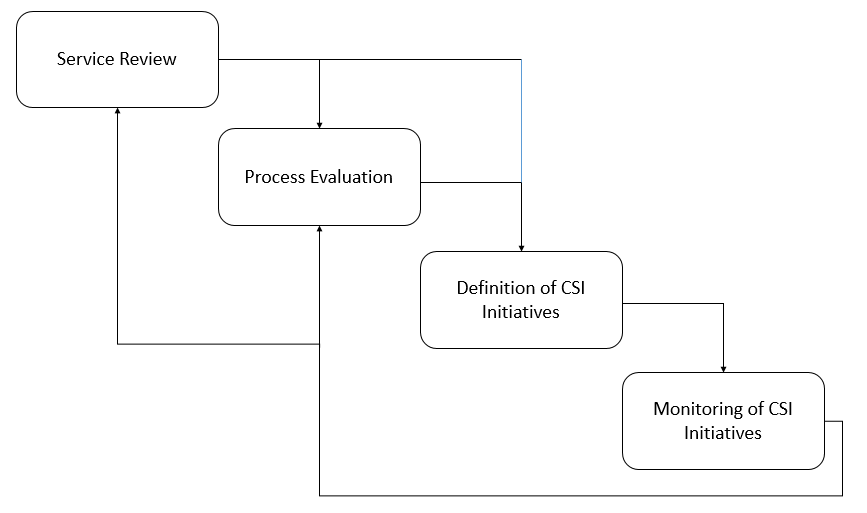
The seven –step improvement process
- Determine what to measure
- Define what to measure
- Conduct gap analysis
- Gather Data
- Data processing
- Analysing data
- How to present and use the information?
- Implement corrective actions
- Integrate CSI with the other stages of the lifecycle
Methods and Techniques
- Activities for delivering CSI
- Perform gap analysis
- Implement benchmarking
- Design and Analyse service measurement frameworks
- Create ROI (Return on Investment)
- Articulating service reporting
- Key metrics
- Technology metrics
- Process metrics
- CSFs and KPIs
- Service metrics
- Initiating a SWOT analysis
- Measure benefits to the business
- Support CSI activities
- Availability Management
- Capability Management
- IT Service Continuity Management
- Problem Management
- Knowledge Management
Organisation and Technology Considerations
- Define roles and responsibilities
- Organisational structure supporting CSI
- Specify tool requirements for implementation success
- Automated incident and problem resolution
- Statistical analysis tools
- Business intelligence and reporting
Implementing Continual Service Improvement
- Key considerations
- Analyse the starting point
- Relating role of governance
- Determine the effect of organisational change
- Construct a communication strategy and plan
- Implementation Challenges and risks
- Establish critical success factors
- KPIs
- Develop risk-benefit analysis

 ENQUIRE
ENQUIRE
 REQUEST CALLBACK
REQUEST CALLBACK
 GET A FREE QUOTE
GET A FREE QUOTE


 Introduction
Introduction Course Details
Course Details Course Content
Course Content



 London
London